About Report Builder
| Platform: | WebMobile |
|---|---|
| Plan Type: | BasicEssentialPremiumEnterprise |
| User Type: | RequesterFull UserAdministrator |
Report Builder lets you build reports with your data in MaintainX®, and visualize them in a table or graph. Your data is grouped by datasets, which you can refine by adding aggregations, filters, dimensions, or formulas to focus on key information.
Report Builder uses data refreshed regularly from multiple sources in your MaintainX organization. You can analyze key data in the application across locations and organizations to gain deeper insights into your organization:
- Part consumption by asset.
- Inventory movement.
- Assets with the most work requests (filtered by location).
- Purchase order costs in a given period (filtered by vendor).
You can build a custom report in the following ways:
- Manually, by selecting data fields and a suitable visualization.
- Using a template with pre-selected data fields and visualization.
Share key information with your organization by adding reports to custom dashboards or exporting the data to PDF or CSV files.
Report Builder Concepts
Datasets
A dataset is a collection of data attached to a specific entity (e.g., parts, work orders, etc.). You can use one or more datasets to build custom reports.
The first dataset you select defines the context of your report. MaintainX automatically shows all datasets connected to your first selection. You can add their columns to your report and build a multi-dimensional report with data coming from different data sources.
MaintainX also automatically shows columns related to the datasets, which expands the scope of your report and impacts how data is aggregated and joined.
Let's say you select the Parts dataset. MaintainX automatically includes any related datasets and adds additional columns (such as Part Area at Location or Part Available Quantity at Location) to show how your data connects across sources. These columns give you more ways to analyze and understand your data. For details, see Datasets.
Formulas
You can create formulas and add them to your report to perform basic calculations and analyze your data. The Report Builder supports formulas such as:
- addition
A + B - subtraction
A - B - multiplication
A * B - division
A / B
Timestamp values only supported subtraction operations, which produce a duration value.
Complex formulas with parentheses, e.g. (A + B)*1.15, are also supported.
When you add a formula to your report, MaintainX assigns letter identifiers to the columns selected before the formula. Identifiers use the same format you find in popular spreadsheet applications-A-Z, then AA, AB, etc. Use the identifiers in formulas to reference specific columns.
You can create formulas using numeric, currency, and timestamp values.
Visualizations
Report Builder provides several visualization types to help you present your data. You can use the following visualization types:
-
Table: shows raw data in rows and columns. For details, see Table Report.
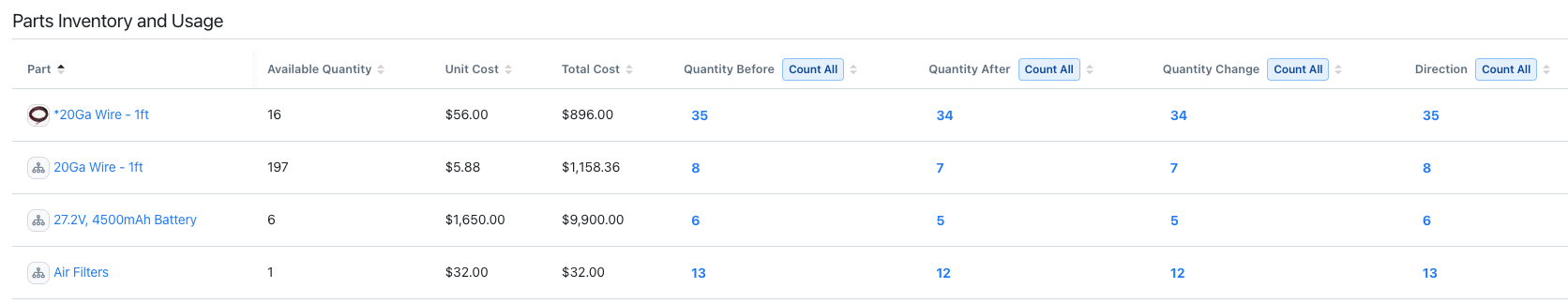
A table report listing parts inventory and usage details -
Graph Reports: provide visual summaries of your data in the following formats:
-
Bar Chart: shows your data using bars and segments to compare quantities across groups.
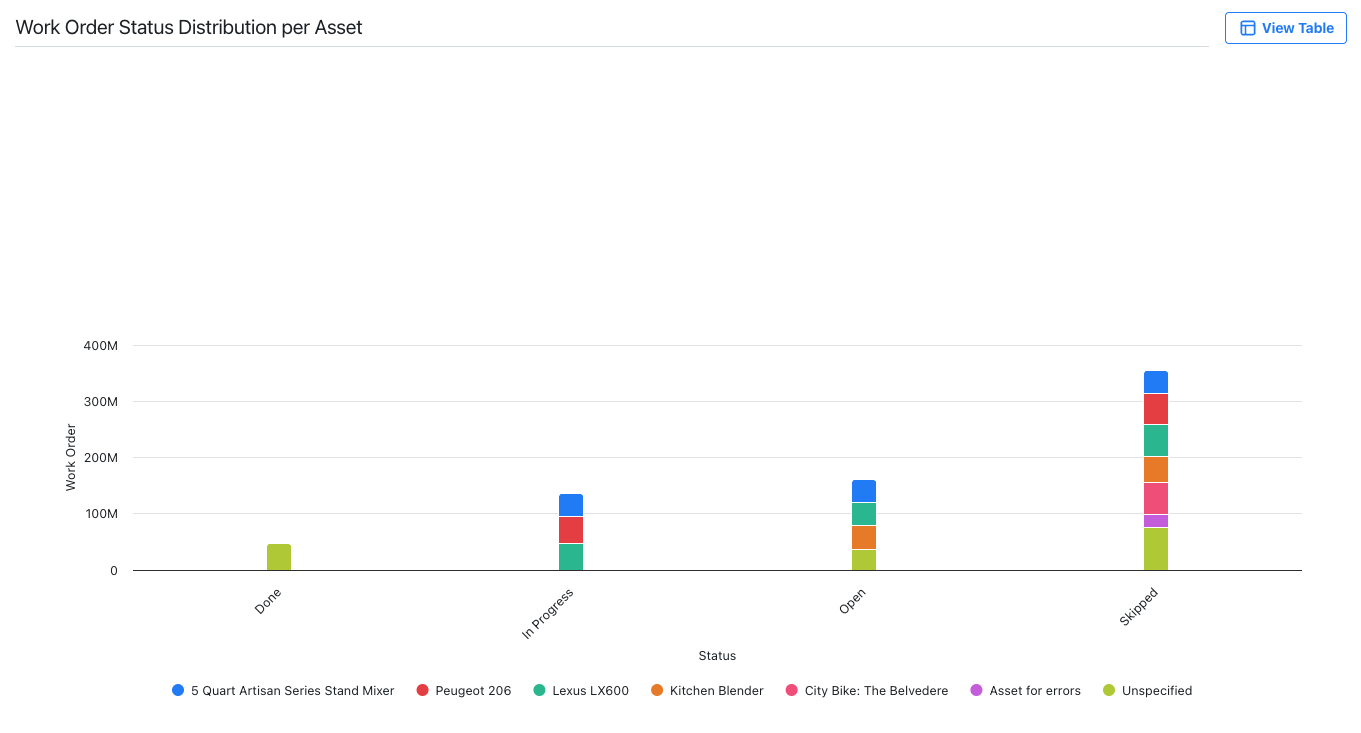
A bar chart displaying the distribution of work order statuses for different assets -
Line Chart: shows trends or changes over time by connecting data points with lines.
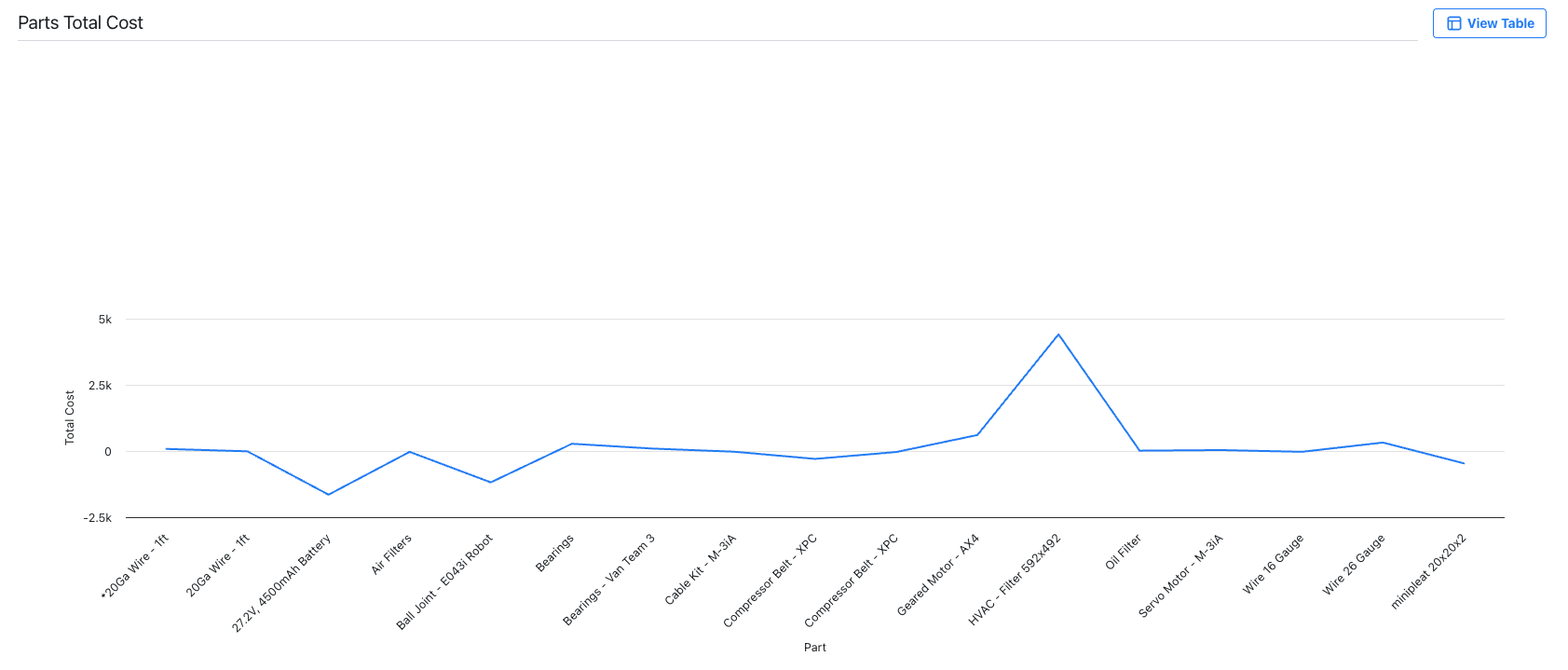
A line chart showing the total cost for various parts -
Pie Chart: shows data as slices of a circle to illustrate part-to-whole relationships.
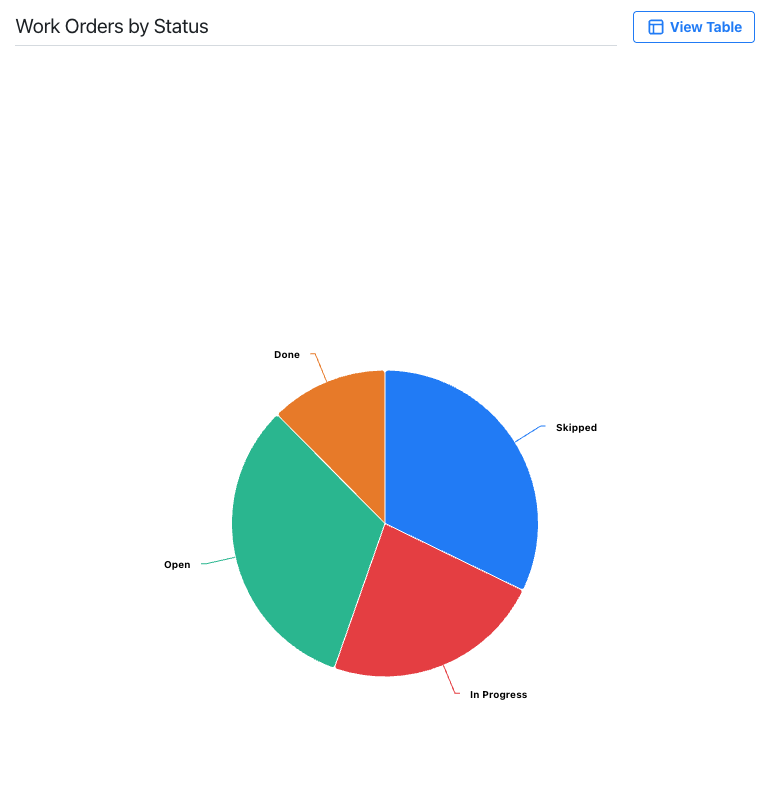
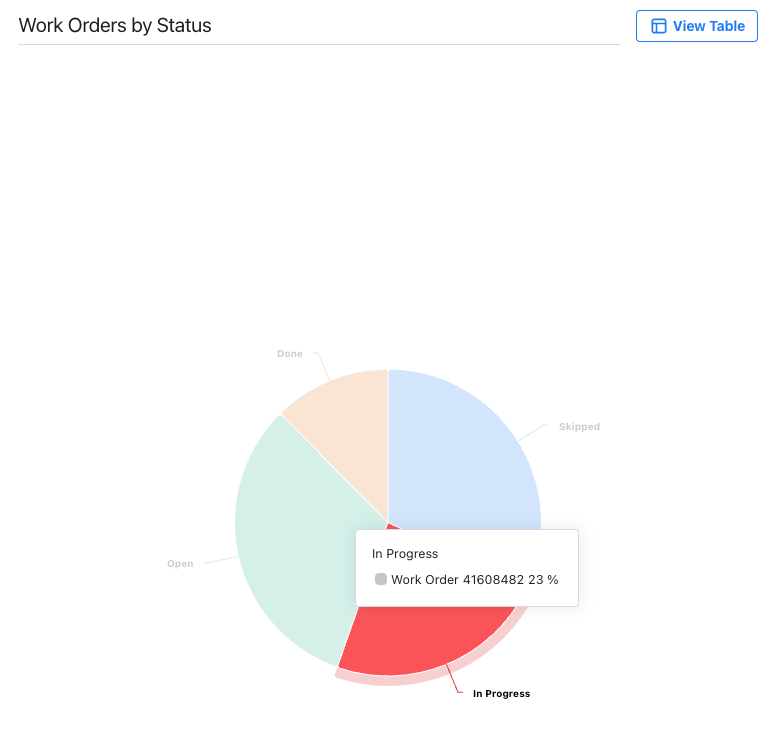
-
For details, see Graph Report.
Visualization Options
After you select a visualization type, you need to tailor the report to focus on the data you want to analyze. The available options depend on the type of visualization you select.
| Visualization Type | Options |
|---|---|
| Table | Aggregation: Select an aggregation to refine the data in your report. |
| Graph: Bar, Line |
|
| Graph: Pie |
|
Aggregations
Aggregations summarize multiple values into a single output to reduce the amount of information displayed in a report. You can use an aggregation like Count, Sum, or Average on your dataset fields to refine how your data is presented.
Primary dataset fields don’t require aggregations, but using one might affect how your data is grouped and displayed.
| Aggregation Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Average | Calculates the mean of all values. For example, if you have three transactions of 5, 10, and 15 parts, the average will be 10. |
| Count (All) | Counts the number of related values. If a part is linked to 5 transactions, the reported value is 5. |
| Count (Unique) | Counts the number of distinct values. If part is used in 3 work orders, 1 time in the first one, 4 times in the second one, and 7 times in the third one, the reported value is 3. |
| Maximum | Gives the largest value. |
| Minimum | Gives the smallest value. |
| Summation | Adds up numeric values from related data. |
You can select an aggregated value to view the underlying source values that were combined, providing more detailed insight into the reported figure.
Date Grouping
The Group By option allows you to group dates by periods: Day, Week, Month, or Year. This option is available for all date columns in Report Builder.
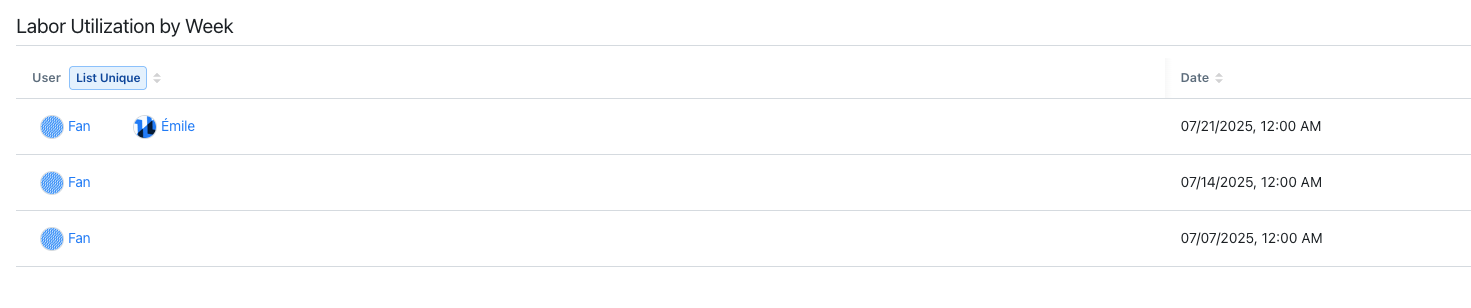
Let's say you want to build a report focused on labor utilization, and group the data by week.
| Dataset | Columns |
|---|---|
| Labor Utilization by Day |
|
- Setting a List (Unique) aggregation on the User column adds one line per user.
- Setting the Group By option to Week groups every occurrence of the user's labor utilization by week, more specifically by the first day of each week at 12:00 AM.
Filter Conditions
Filter conditions determine what makes the selected column in your report match the filter.
| Condition | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Is one of | Finds entities where the filter field matches one or more values that you specify. | Use this to include specific entities in the view. |
| Is empty | Finds entities where the filter field has no value at all. | |
| Is not empty | Finds entities where the filter field has any value. | |
| Contains | Finds entities that contain the selected value. | |
| Does not contain | Finds entities that don't contain the selected value. | |
| Is equal to | Finds entities that match the selected value. | |
| Is not equal to | Finds entities that have a different value than the one selected. | |
| Is above | Finds entities that have a greater numeric value than the one selected. | |
| Is above or equal to | Finds entities that have an equal or greater numeric value than the one selected. | |
| Is below | Finds entities that have a smaller numeric value than the one selected. | |
| Is below or equal to | Finds entities that have an equal or smaller numeric value than the one selected. | |
| Is between | Finds entities that have a date value within a specific range. |
Global Report Builder
If you have a Global Organization, you can build global custom reports to analyze data across all your sub-organizations, compare key metrics, and share insights with your team.
- For details, see Build a Global Custom Report.
- For more information about Global Organizations, see About Global Organizations.
Building a global custom report is identical to building a custom report for a single sub-organization. The only difference is the Organization column, which appears when you create a global custom report.
You can:
- Apply filters to choose which sub-organizations to include in your report.
- Access and analyze the selected sub-organizations' combined data.
When you build a global custom report, you can add entities (e.g. work orders, parts) that belong to a sub-organization. If you have sufficient permission to view the sub-organization's entities, you can select an entity from the Preview panel to view its details. Otherwise, you will not be able to access it and view its details.
Global Report Builder Limitations
-
You can view only specific entities' details if they belong to a sub-organization you have permission to view:
- Location
- Manufacturer
- Model
- Part
- Purchase order
- Request
- Tag
- Team
- Vendor
- Work order
-
You can't select Users.
-
Entities from different sub-organizations might have the same name. Use the Organization column to distinguish them.